The Impact of a Child’s Addiction on Parents: Navigating the Emotional Landscape
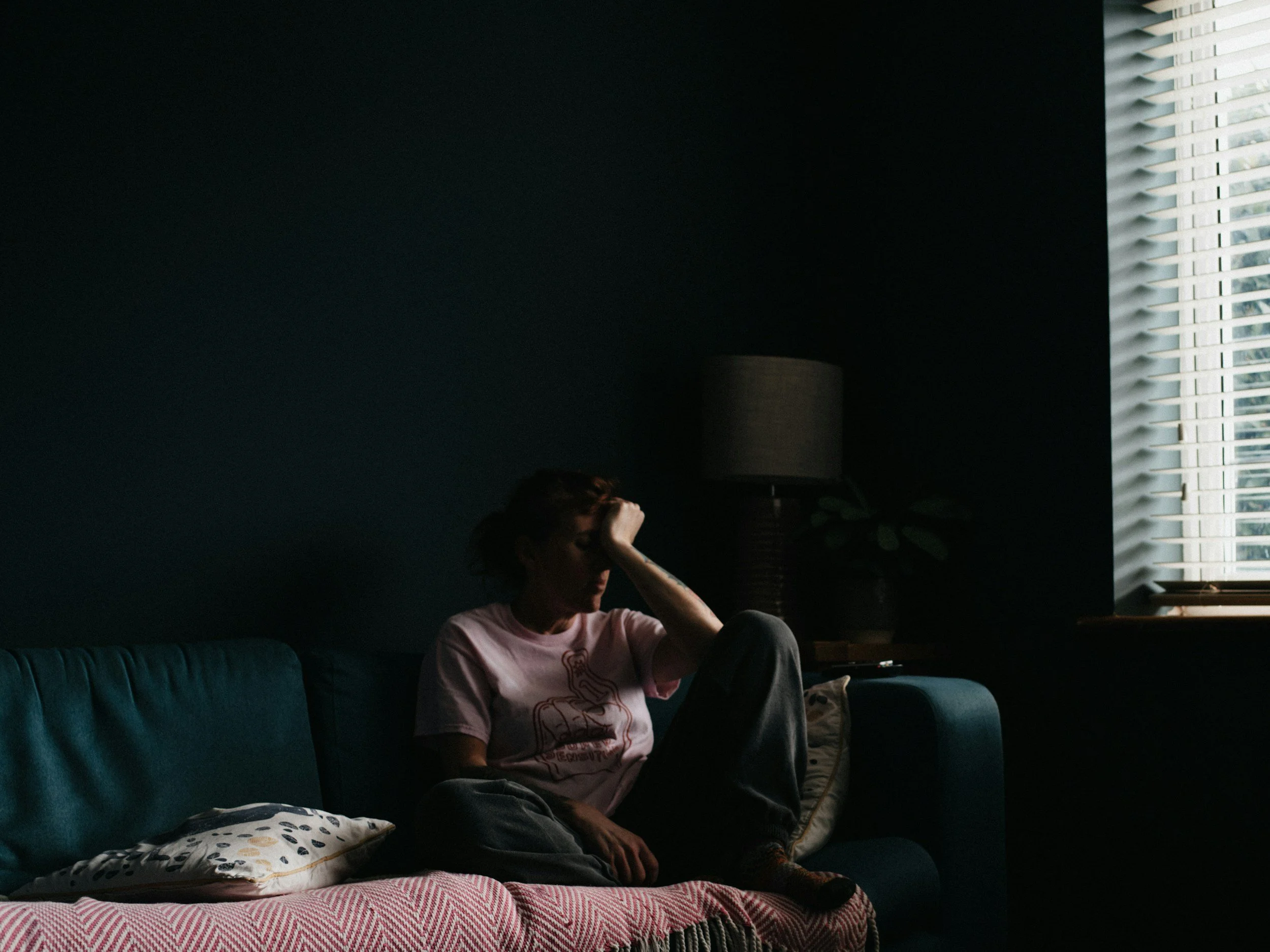
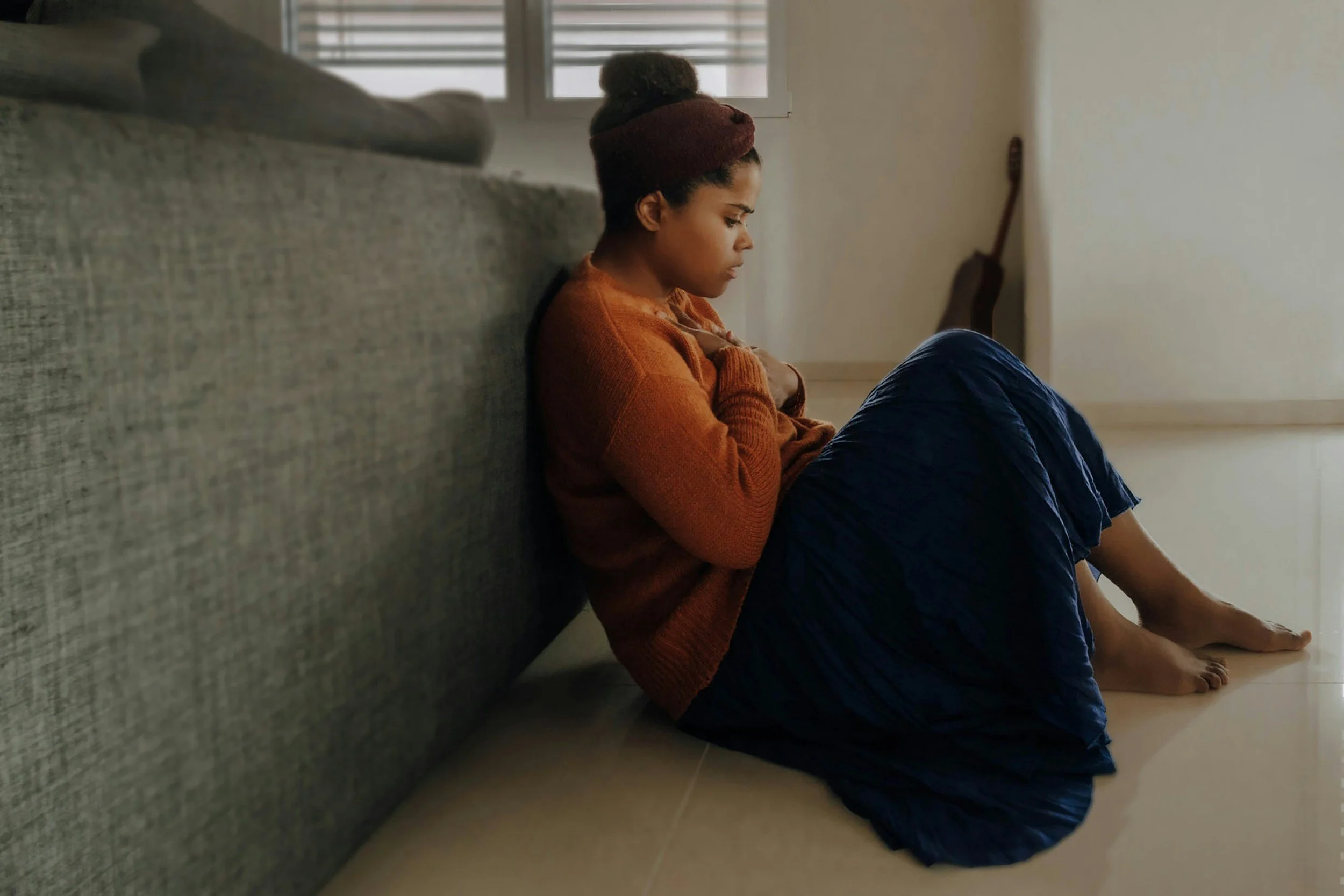
When a child struggles with addiction, it profoundly affects the entire family, particularly the parents. The emotional toll can be overwhelming, as parents grapple with feelings of helplessness, guilt, and concern for their child's future. This blog explores the various impacts on parents when a child faces addiction, offering insights and coping strategies.
The Emotional Toll on Parents
1. Guilt and Shame
Self-Blame: Many parents question their parenting choices, wondering if they could have done something differently to prevent their child's addiction.
Stigma: The stigma surrounding addiction can lead parents to feel isolated and ashamed, making it difficult to seek support.
2. Anxiety and Fear
Uncertainty: Parents often worry about their child's well-being, fearing for their safety and future.
Health Risks: Concerns about physical health, legal issues, or even the possibility of overdose can create constant anxiety.
3. Sadness and Grief
Loss of Dreams: Parents may mourn the loss of the future they envisioned for their child, feeling sadness over missed milestones and opportunities.
Emotional Withdrawal: The ongoing struggle with addiction can lead to disconnection within the family, causing further grief.
The Strain on Relationships
1. Marital Stress
Conflict: Differing approaches to handling the child's addiction can lead to conflict between partners, straining the marital relationship.
Isolation: Parents may find themselves emotionally distant from each other as they cope with their own feelings of fear and sadness.
2. Siblings’ Impact
Neglect: Siblings may feel overlooked or neglected as parents focus on the child with addiction, leading to feelings of resentment or abandonment.
Emotional Burden: Siblings may also carry the emotional weight of their brother or sister’s struggles, affecting their own mental health.
Physical and Mental Health Consequences
1. Stress-Related Health Issues
Physical Symptoms: Chronic stress can lead to headaches, fatigue, and other physical ailments.
Mental Health: Parents are at a higher risk for anxiety disorders and depression, which may require professional intervention.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Neglecting Self-Care: Parents may prioritize their child’s needs over their own, leading to poor self-care habits and declining health.
Increased Substance Use: Some parents may turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms, including alcohol or medication misuse.
Coping Strategies for Parents
1. Seek Support
Support Groups: Connecting with other parents facing similar challenges can provide comfort and understanding.
Professional Help: Therapists and counselors specializing in addiction can offer valuable coping strategies.
2. Educate Yourself
Understanding Addiction: Learning about addiction can help parents recognize that it is a complex disease, reducing feelings of shame and guilt.
Resources: Utilize books, websites, and workshops focused on addiction recovery.
3. Establish Boundaries
Healthy Limits: Setting boundaries can protect parents’ emotional and physical well-being, allowing them to support their child without sacrificing their health.
Encourage Independence: Allowing the child to take responsibility for their recovery can empower them and relieve some pressure from parents.
4. Practice Self-Care
Prioritize Well-Being: Engaging in regular exercise, healthy eating, and relaxation techniques can help parents manage stress.
Personal Interests: Pursuing hobbies and interests can provide a sense of joy and fulfillment outside of the family dynamic.
Conclusion
The journey of parenting a child with addiction is fraught with challenges, but understanding the emotional impacts can help parents navigate this difficult terrain. By seeking support, prioritizing self-care, and establishing healthy boundaries, parents can foster resilience for themselves and their families.
Understanding Women's Trauma Suppression: Impacts on the Body and Mind
Women have long been the silent bearers of trauma, often suppressing their experiences to navigate societal expectations and personal struggles. This blog delves into the intricate relationship between trauma suppression and its effects on women's physical and mental health.
The Nature of Trauma in Women's Lives
Trauma can stem from various sources, including:
Personal Experiences: Abuse, assault, loss, or significant life changes.
Cultural and Societal Pressures: Gender roles, discrimination, and societal expectations can exacerbate feelings of inadequacy and fear.
Intergenerational Trauma: Women may carry the burdens of trauma experienced by their mothers and grandmothers, affecting their emotional and physical well-being.
The Cycle of Suppression
Many women feel compelled to suppress their trauma due to:
Stigma: Fear of judgment or disbelief can lead to silence.
Coping Mechanisms: Some may believe that ignoring their pain is a way to manage it.
Role Expectations: The pressure to appear strong or composed can prevent open discussions about mental health.
Impacts on the Body
Suppressing trauma doesn’t just affect mental health; it manifests physically in several ways:
1. Chronic Pain
Muscle Tension: Emotional stress can lead to physical tension, resulting in chronic pain conditions like fibromyalgia.
Headaches: Stress-related tension can trigger migraines and chronic headaches.
2. Digestive Issues
Gut-Brain Connection: Trauma can disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to conditions like IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome).
Eating Disorders: Some women may develop unhealthy eating patterns as a means of coping.
3. Hormonal Imbalances
Stress Hormones: Prolonged trauma can lead to elevated cortisol levels, affecting menstrual cycles and overall hormonal balance.
Reproductive Health: Women may experience fertility issues or complications during pregnancy due to unresolved trauma.
4. Immune System Suppression
Increased Illness: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making women more susceptible to illnesses.
Mental Health Consequences
The psychological impacts of trauma suppression can be profound:
Anxiety and Depression: Unaddressed trauma can lead to chronic anxiety or depressive disorders.
PTSD: Women may develop Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, characterized by flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety.
Low Self-Esteem: Ongoing feelings of guilt or shame can diminish self-worth and confidence.
Breaking the Cycle
Addressing suppressed trauma is crucial for healing. Here are some strategies:
1. Therapy and Counseling
Professional Support: Speaking with a therapist can help women process their experiences in a safe environment.
Group Therapy: Sharing experiences with others can foster a sense of community and understanding.
2. Mindfulness and Meditation
Stress Relief: Practices like yoga and meditation can help women reconnect with their bodies and manage stress.
3. Physical Activity
Exercise: Regular physical activity can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, improving overall well-being.
4. Open Conversations
Breaking the Silence: Encouraging open discussions about trauma can help normalize the experiences and reduce stigma.
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing trauma is essential for women’s overall health and well-being. By breaking the cycle of suppression, women can reclaim their narratives, heal, and thrive. It's vital to foster an environment where voices can be heard, and healing can begin.
The Healing Power of Sound: Exploring Sound Therapy
In recent years, the concept of sound therapy has gained significant traction as a holistic approach to healing and wellness. From ancient practices to contemporary techniques, sound has been recognized for its therapeutic properties. In this blog, we’ll explore how sound can promote healing, the science behind it, and various methods to incorporate sound into your wellness routine.
What is Sound Healing?
Sound healing is a therapeutic practice that uses sound waves to improve physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being. It involves various techniques and tools, including:
Singing Bowls: Often made of metal or crystal, these bowls produce resonant tones when struck or rubbed, promoting relaxation and balance.
Tuning Forks: These devices emit specific frequencies that can help align the body's energy and release tension.
Gongs: The deep, rich tones of gongs can create a profound sense of tranquility and facilitate emotional release.
Voice: Chanting, toning, and singing can be powerful tools for self-expression and healing.
How Sound Affects Us
1. Vibrational Resonance
Every cell in our body vibrates at a specific frequency. When we are healthy, these frequencies are in harmony. However, stress, illness, or emotional turmoil can disrupt this balance. Sound therapy utilizes vibrations to restore harmony, promoting healing on a cellular level.
2. Brainwave Entrainment
Sound can influence brainwave patterns, affecting our state of consciousness. Different frequencies can promote relaxation, focus, or deep meditation. For instance, binaural beats—a technique using two slightly different frequencies in each ear—can aid in achieving deep states of relaxation and focus.
3. Emotional Release
Sound can evoke powerful emotions, helping individuals process feelings that may be suppressed. Listening to or creating music can facilitate emotional release, allowing for healing and self-discovery.
4. Stress Reduction
Research shows that sound therapy can reduce stress and anxiety levels. Listening to calming sounds, such as nature sounds or gentle music, can lower cortisol levels and promote relaxation.
Methods of Sound Healing
1. Sound Baths
A sound bath involves immersing participants in sound waves created by various instruments, such as singing bowls, gongs, and chimes. Participants typically lie down comfortably while the sounds envelop them, promoting deep relaxation and healing.
2. Guided Meditations with Sound
Incorporating sound into guided meditations can enhance the experience. Soft, soothing music or nature sounds can help participants enter a meditative state more easily, facilitating relaxation and mindfulness.
3. Personal Sound Practice
You don’t need to be a trained practitioner to benefit from sound healing. Here are some simple practices you can incorporate into your daily routine:
Listening to Music: Create playlists with music that resonates with you. Genres like classical, ambient, or nature sounds can promote relaxation.
Chanting or Toning: Experiment with your voice. Chanting simple mantras or toning specific sounds can create a sense of grounding and connection.
Playing Instruments: If you play an instrument, take time to explore improvisation. The act of creating sound can be cathartic and healing.
Scientific Insights
While sound therapy has ancient roots, modern science is beginning to validate its benefits. Studies have shown that sound therapy can:
Reduce anxiety and depression.
Improve sleep quality.
Enhance cognitive function and focus.
Promote physical healing by lowering blood pressure and heart rate.
Conclusion
Sound has an incredible ability to heal and transform. Whether you explore sound baths, guided meditations, or personal sound practices, integrating sound into your wellness routine can enhance your overall well-being.
As you embark on your sound healing journey, keep an open mind and allow yourself to explore the transformative power of sound.
Understanding Menstrual Cycles and Their Impact on Mental Health
Menstruation is a natural process that affects half the world's population, yet it remains a topic often shrouded in stigma and misunderstanding. Beyond the physical symptoms, menstrual cycles can significantly impact mental health. In this blog, we’ll explore the connection between menstrual cycles and mental well-being, shedding light on the emotional and psychological effects that may accompany this monthly phenomenon.
The Menstrual Cycle Explained
A typical menstrual cycle lasts about 28 days, although it can range from 21 to 35 days. The cycle comprises several phases:
Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5): Shedding of the uterine lining (the bleed phase); symptoms may include cramps, fatigue, and mood changes.
Follicular Phase (Days 6-14): Hormones rise, leading to increased energy and mood improvement as the body prepares for ovulation.
Ovulation (Around Day 14): The release of an egg; many experience a peak in energy and libido.
Luteal Phase (Days 15-28): Hormonal fluctuations can lead to premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms, including mood swings, irritability, and anxiety.
How Menstrual Cycles Affect Mental Health
1. Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle. These changes can influence neurotransmitters like serotonin, which regulates mood. For some, the luteal phase may bring about feelings of sadness, anxiety, or irritability, contributing to conditions like premenstrual syndrome (PMS) or premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD).
2. Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms of menstruation—such as cramps, bloating, and fatigue—can impact mental health. Chronic pain or discomfort can lead to irritability, anxiety, and decreased motivation, affecting overall well-being and daily functioning.
3. Social and Cultural Factors
Cultural stigma surrounding menstruation can exacerbate feelings of shame or embarrassment, leading to mental health challenges. Women may feel isolated or unsupported, particularly if they lack access to menstrual hygiene products or education about their bodies.
4. Impact on Daily Life
Menstrual cycles can affect daily activities, including work and social interactions. Women may find it challenging to participate in activities or meet responsibilities during their periods, leading to feelings of inadequacy or frustration.
Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Help
Understanding the emotional and psychological symptoms associated with menstrual cycles is vital. Common signs include:
Mood swings
Anxiety or depression
Irritability
Fatigue
Changes in sleep patterns
If these symptoms are severe or disruptive, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare provider. They can help assess the situation and suggest appropriate treatment options, which may include lifestyle changes, therapy, or medication.
Tips for Managing Mental Health During Menstruation
Track Your Cycle: Keeping a menstrual diary can help you identify patterns and triggers related to mood changes. This awareness can empower you to manage symptoms more effectively.
Practice Self-Care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as yoga, meditation, or gentle exercise. These practices can help alleviate stress and improve mood.
Maintain a Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet can influence mood. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, complex carbohydrates, and vitamins can help regulate mood swings.
Connect with Others: Sharing experiences with friends or support groups can reduce feelings of isolation and provide reassurance.
Seek Professional Support: If menstrual-related symptoms significantly impact your life, consider speaking with a mental health professional or a gynecologist who understands the connection between menstrual health and mental well-being.
Conclusion
The interplay between menstrual cycles and mental health is complex and varies from person to person. By recognizing the impact of hormonal changes and physical symptoms, we can foster a greater understanding of this natural process and its effects on mental well-being.
Let’s continue to break the stigma around menstruation, encouraging open conversations and supporting one another in our journeys toward better mental health.
Understanding Self-Sabotage: The Psychology Behind Our Own Worst Enemy
Self-sabotage is a term that resonates with many of us. Whether it’s procrastinating on important tasks, undermining our relationships, or setting goals only to abandon them, we often find ourselves getting in our own way. But why do we do this? Let's dive into the psychology behind self-sabotage and explore how we can overcome it.
What is Self-Sabotage?
Self-sabotage refers to behaviors or thought patterns that hinder our progress and success. It often manifests in various forms, such as:
Procrastination: Delaying tasks despite knowing they are important.
Negative Self-Talk: Criticizing oneself, leading to decreased confidence.
Fear of Success: Avoiding opportunities that could lead to personal growth or recognition.
The Psychological Roots of Self-Sabotage
1. Fear of Failure
At the core of self-sabotage is often a deep-seated fear of failure. This fear can stem from past experiences where failure led to embarrassment or disappointment. As a protective mechanism, individuals may sabotage their efforts to avoid the possibility of failing again.
2. Imposter Syndrome
Many people experience imposter syndrome, where they doubt their accomplishments and fear being exposed as a “fraud.” This feeling can lead to self-sabotage, as individuals may unconsciously undermine their success to align with their self-perception.
3. Low Self-Esteem
Individuals with low self-esteem may believe they are unworthy of success or happiness. This belief can manifest in self-sabotaging behaviors, as they may feel they don’t deserve to achieve their goals.
4. Comfort Zones
Change can be intimidating, even if the current situation is not ideal. Self-sabotage can serve as a way to remain in a familiar, albeit uncomfortable, zone. The fear of the unknown can prevent individuals from pursuing new opportunities.
The Cycle of Self-Sabotage
Self-sabotaging behaviors often create a vicious cycle:
Trigger: A situation arises that challenges you (e.g., a work project).
Response: You engage in self-sabotaging behavior (e.g., procrastination).
Outcome: The project suffers, reinforcing negative beliefs about your abilities.
Reinforcement: This cycle repeats, making it harder to break free.
Overcoming Self-Sabotage
1. Awareness and Reflection
The first step to overcoming self-sabotage is recognizing it. Reflect on your behaviors and thought patterns. Journaling can be a helpful tool to document moments of self-sabotage and explore their triggers.
2. Challenge Negative Thoughts
Practice reframing negative self-talk. Instead of thinking, “I’ll never get this done,” try, “I can take small steps to complete this task.” Challenging these thoughts can help build a more positive mindset.
3. Set Realistic Goals
Break down larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks. This can reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed and make it easier to take action.
4. Seek Support
Talking about your feelings with friends, family, or a professional can provide valuable insights and encouragement. Support systems can help hold you accountable and provide motivation.
5. Practice Self-Compassion
Be kind to yourself. Understand that everyone makes mistakes and faces challenges. Practicing self-compassion can reduce the fear of failure and create a healthier relationship with yourself.
Conclusion
Self-sabotage is a common struggle that can stem from various psychological factors. By understanding the roots of these behaviors and implementing strategies to counteract them, you can break free from the cycle of self-sabotage.
Struggling in Isolation: Navigating the Challenges of Disconnection
In a world bustling with activity, it’s ironic how isolation can creep in, often unnoticed. Many individuals find themselves feeling increasingly disconnected, even when surrounded by others. This experience, though common, can lead to profound feelings of loneliness and emotional distress.
The Reality of Isolation
Isolation can manifest in various ways—social, emotional, or even physical. It often begins subtly, with small feelings of disconnection that can grow over time. As people navigate their daily lives, they may find themselves withdrawing from social interactions, neglecting hobbies, or feeling overwhelmed by anxiety and sadness. This gradual shift can create a cycle where the more isolated one feels, the harder it is to reach out for connection.
Signs of Isolation
- Increased Loneliness: A pervasive sense of being cut off from friends, family, or community.
- Emotional Distress: Heightened feelings of anxiety, sadness, or irritability becoming more frequent.
- Withdrawal: A tendency to avoid social engagements and activities that once brought joy.
- Physical Symptoms: Changes in sleep patterns, appetite, or overall energy levels.
The Impact of Isolation
Prolonged isolation can have significant consequences on mental and physical health. Research indicates that social isolation can lead to:
- Mental Health Issues: Increased risk of anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders.
- Physical Health Risks: Weakened immune function, cardiovascular problems, and other chronic health conditions.
- Cognitive Decline: Impaired memory and cognitive function due to lack of social engagement.
Strategies for Connection
While the struggle with isolation can feel daunting, there are actionable steps individuals can take to foster connection and support their well-being:
1. Reach Out
- Connect with Loved Ones: Initiating contact with friends or family can be a powerful step. A simple text, phone call, or video chat can rekindle connections and provide emotional support.
- Join Online Communities or In Person: Groups or forums centered around shared interests can create a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation.
2. Engage in Activities
- Pursue Hobbies: Rediscovering interests or engaging in new activities can provide a much-needed distraction and boost overall mood.
- Volunteer Virtually: Offering time to a cause can foster a sense of purpose and connection, helping to combat feelings of isolation.
3. Practice Mindfulness and Self-Compassion
- Mindfulness Techniques: Engaging in meditation, yoga, or relaxation exercises can help ground individuals and alleviate anxiety.
- Self-Compassion: Acknowledging and accepting feelings of isolation without judgment is a crucial step toward healing.
4. Seek Professional Support
- Therapy or Counselling: For those feeling overwhelmed, consulting a mental health professional can provide a safe space to explore feelings and develop coping strategies.
Moving Toward Connection
While struggling in isolation can be challenging, it’s essential to remember that connection is possible. Taking proactive steps to engage with others, rediscovering hobbies, practicing mindfulness, and seeking support can lead to meaningful change.
Isolation does not have to define one’s experience. By recognizing the signs and taking steps toward connection, individuals can navigate the challenges of isolation and find hope in their journey.
If you or someone you know is struggling with feelings of isolation, consider reaching out for support. There are resources available, and taking that first step can lead to a brighter, more connected future.
Understanding Mom Rage: Causes, Effects, and Coping Strategies
Mom rage is a term that has gained traction in recent years, shedding light on the intense feelings of anger and frustration many mothers experience. As the demands of parenting can often feel overwhelming, it’s important to understand the roots of these emotions and how to manage them effectively.
What is Mom Rage?
Mom rage refers to the feelings of anger, frustration, and exhaustion that many mothers experience in response to the daily challenges of parenting. It can manifest as irritability, outbursts, or a sense of being overwhelmed, often arising from the stressors of juggling multiple responsibilities.
Common Triggers of Mom Rage
Overwhelm from Responsibilities: Balancing parenting duties, work, household chores, and personal life can lead to feelings of being stretched too thin.
Lack of Support: Feeling unsupported by partners, family, or friends can contribute to feelings of isolation and frustration.
Sleep Deprivation: Exhaustion from sleepless nights can significantly impact mood and patience.
Unrealistic Expectations: The pressure to be a perfect parent can create feelings of inadequacy and anger when things don’t go as planned.
Comparison: Social media can amplify feelings of inadequacy as mothers compare their experiences to those of others.
The Impact of Mom Rage
On Mothers
Emotional Toll: Frequent feelings of rage can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and depression.
Physical Health: Chronic stress can contribute to various health issues, including fatigue, headaches, and digestive problems.
On Children
Emotional Effects: Children may feel scared or confused when witnessing their mother’s anger, which can impact their emotional development.
Behavioral Issues: Reacting with anger can lead to children mimicking these behaviors, resulting in increased conflict and misunderstandings.
On Relationships
Strained Partnerships: Unmanaged anger can create tension between partners, leading to arguments and a lack of support.
Social Isolation: Mothers may withdraw from friendships or supportive networks due to feelings of shame or inadequacy.
Coping Strategies for Mom Rage
1. Acknowledge Your Feelings
Recognize that feeling angry is valid and normal. Allow yourself to experience and express these emotions without guilt.
2. Identify Triggers
Keep a journal to track when feelings of rage occur. Understanding your triggers can help you anticipate and manage your responses.
3. Practice Self-Care
Prioritize time for yourself. Whether it’s a short walk, reading a book, or engaging in a hobby, self-care is essential for emotional well-being.
4. Communicate Openly
Share your feelings with your partner or a trusted friend. Open communication can foster understanding and support.
5. Seek Professional Help
If feelings of rage become overwhelming, consider talking to a therapist. Professional guidance can provide tools and strategies for managing emotions.
6. Develop Coping Techniques
Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as deep breathing and mindfulness can help ground you in moments of stress.
Physical Activity: Exercise can be a great outlet for pent-up frustration and improve overall mood.
7. Set Realistic Expectations
Let go of the idea of perfection. Understand that parenting is a journey filled with ups and downs.
Conclusion
Mom rage is a common experience that many mothers face, often stemming from the pressures of parenting. By acknowledging these feelings, identifying triggers, and implementing coping strategies, mothers can navigate their emotions more effectively. It’s crucial to remember that seeking support is not a sign of weakness but a vital step toward emotional well-being.
Understanding Narcissism: Traits, Impacts, and Pathways to Healing
Narcissism is a term that often gets thrown around in casual conversation, but it encompasses a complex set of traits and behaviors. Understanding narcissism—both at the individual and relational levels—can shed light on its effects on mental health and interpersonal relationships.
What is Narcissism?
Narcissism is characterized by an excessive sense of self-importance, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy for others. It exists on a spectrum, ranging from healthy self-confidence to narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), which is a more severe and pervasive form of narcissism.
Key Traits of Narcissism
Grandiosity: An exaggerated sense of self-importance and an inflated view of one’s talents or achievements.
Need for Admiration: A constant craving for validation and appreciation from others.
Lack of Empathy: Difficulty understanding or caring about the feelings and needs of others.
Manipulative Behavior: Using others for personal gain or to maintain one’s self-image.
Entitlement: A belief that one deserves special treatment and that rules don’t apply to them.
Types of Narcissism
Grandiose Narcissism: Characterized by overt arrogance, dominance, and a strong need for admiration.
Vulnerable Narcissism: Involves more covert behaviors such as insecurity, defensiveness, and hypersensitivity to criticism.
The Impact of Narcissism
On Individuals
Relationships: Narcissists often struggle to maintain healthy relationships due to their self-centeredness and lack of empathy. Partners may feel undervalued or manipulated.
Mental Health: While narcissists may appear confident, they often experience underlying issues such as anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
On Families
Toxic Dynamics: Narcissistic behavior can create a hostile or unstable home environment, leading to emotional distress for family members.
Parenting Challenges: Narcissistic parents may prioritize their needs over their children’s, resulting in unhealthy emotional development.
On Workplaces
Team Dysfunction: Narcissistic individuals can disrupt team dynamics, leading to conflict and reduced morale.
Leadership Issues: While some narcissists may rise to leadership positions, their lack of empathy can hinder effective team management and collaboration.
Pathways to Healing
For Individuals with Narcissistic Traits
Self-Reflection: Engaging in introspection can help narcissists recognize their behaviors and the impact they have on others.
Therapy: Professional help, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can assist individuals in addressing underlying issues and developing healthier coping strategies.
For Those Affected by Narcissism
Set Boundaries: Establish clear boundaries to protect your emotional well-being and maintain a sense of self.
Seek Support: Connect with supportive friends, family, or therapists who can provide validation and understanding.
Educate Yourself: Understanding narcissism can help you navigate interactions and foster resilience.
Building Healthier Relationships
Practice Empathy: Encourage open communication and try to understand the underlying feelings of both yourself and the narcissist.
Focus on Self-Care: Prioritize your mental and emotional health through activities that bring you joy and fulfillment.
Conclusion
Narcissism, while often misunderstood, plays a significant role in many individuals' lives and relationships. By gaining insight into narcissistic traits, the impact they have, and pathways to healing, both narcissists and those affected by narcissistic behavior can work towards healthier interactions and emotional well-being.
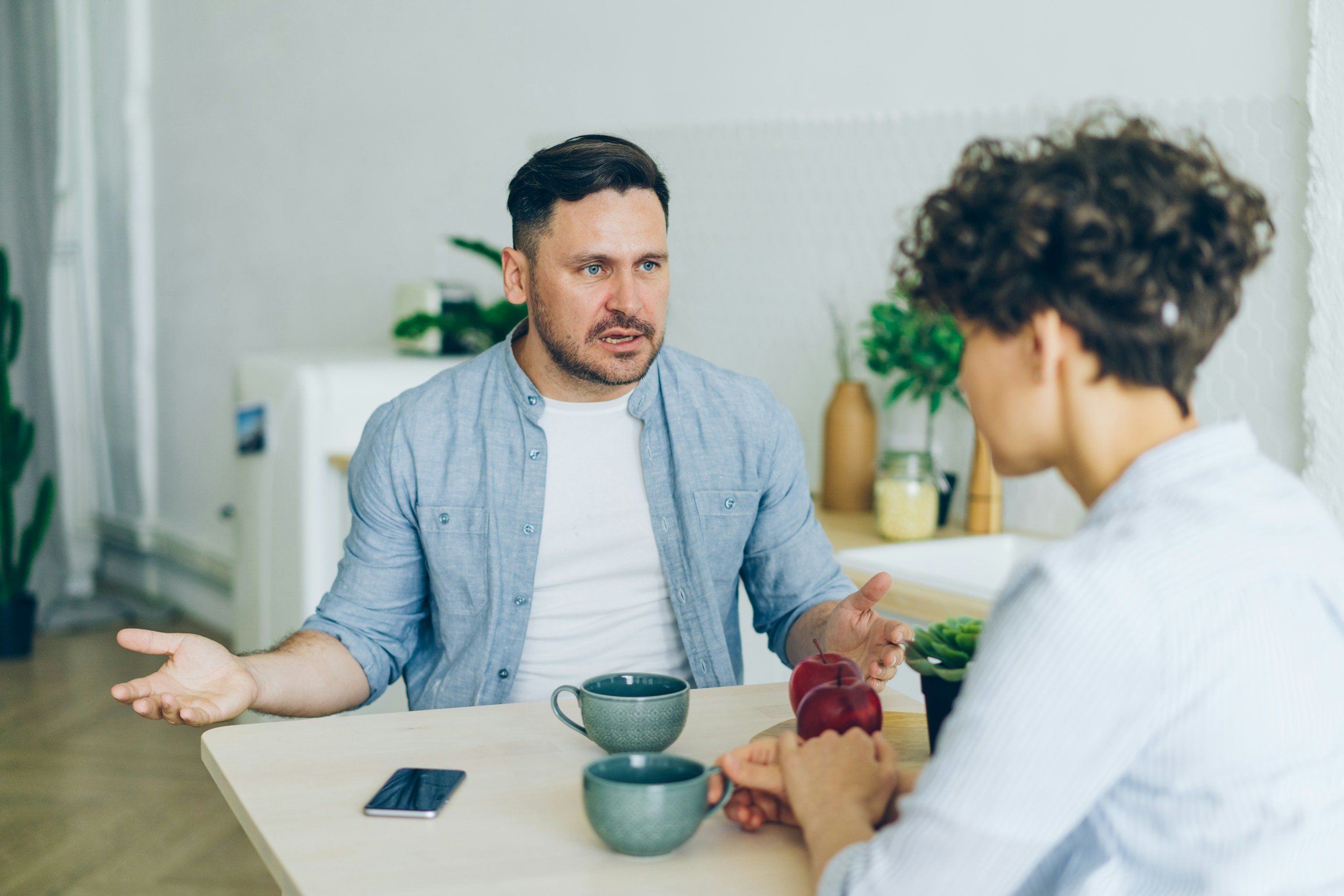
Navigating High Conflict Couples: Understanding and Strategies for Resolution
High conflict couples often find themselves in a cycle of intense disputes that can be emotionally draining and damaging to their relationship. Understanding the dynamics at play and learning effective strategies for resolution can help these couples find healthier ways to communicate and connect.
Understanding High Conflict Dynamics
1. Characteristics of High Conflict Couples
Frequent Arguments: These couples often engage in intense and recurring disagreements.
Emotional Escalation: Conflicts can escalate quickly, leading to heightened emotions and distress.
Negative Communication Patterns: Criticism, contempt, defensiveness, and stonewalling are common.
Difficulties in Resolution: High conflict couples struggle to resolve disputes and may revert to old patterns repeatedly.
2. Underlying Causes
Personality Differences: Differing personality traits can lead to misunderstandings and conflict.
Unresolved Past Issues: Previous grievances can resurface, complicating current disputes.
Stressful Life Events: External stressors (like jobs, finances, or family issues) can exacerbate conflicts.
Poor Communication Skills: Many high conflict couples lack effective communication tools, leading to misunderstandings.
Strategies for Resolution
1. Effective Communication
Active Listening: Each partner should practice listening without interrupting. Acknowledge each other’s feelings.
Use “I” Statements: Express feelings and needs using “I” statements (e.g., “I feel upset when…”), rather than blaming the other.
Stay Calm: Maintain a calm tone and body language to prevent escalation.
2. Identify Patterns
Recognize Triggers: Identify what triggers conflicts and work to avoid these situations or address them constructively.
Reflect on Past Conflicts: Discuss previous disagreements to understand recurring themes and patterns.
3. Seek Professional Help
Couples Therapy: A trained therapist can provide tools and strategies tailored to the couple’s unique dynamics.
Workshops and Support Groups: Engaging in these can offer new perspectives and support.
4. Create a Conflict Resolution Plan
Set Ground Rules: Establish rules for discussions, such as no name-calling or yelling.
Time-Outs: Agree to take breaks during heated arguments to cool down and reflect before continuing the discussion.
Focus on Solutions: Shift the focus from blame to finding constructive solutions that work for both partners.
Building a Healthier Relationship
1. Foster Connection
Quality Time: Regularly spend time together doing enjoyable activities to strengthen the emotional bond.
Express Appreciation: Regularly acknowledge and appreciate each other’s strengths and efforts.
2. Develop Emotional Intelligence
Self-Awareness: Each partner should work on understanding their emotions and triggers.
Empathy: Practicing empathy can help partners understand each other’s perspectives better.
3. Establish Boundaries
Respect Personal Space: Allow each other space to process emotions without feeling pressured to resolve issues immediately.
Know When to Walk Away: If a conversation becomes too heated, agree to pause and revisit the discussion later.
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges of being a high conflict couple can be daunting, but with the right tools and strategies, it is possible to foster a healthier relationship. By focusing on effective communication, understanding individual triggers, and seeking professional help when needed, couples can break the cycle of conflict and build a stronger, more resilient partnership.
Overcoming Infidelity in a Relationship: Is Staying Together the Right Choice?
Infidelity is one of the most challenging experiences a couple can face, often shaking the very foundation of trust and commitment in a relationship. Discovering that your partner has been unfaithful can lead to a whirlwind of emotions, including betrayal, anger, sadness, and confusion. However, many couples find a way to navigate through this tumultuous time and emerge stronger. In this blog, we’ll explore how to overcome infidelity, the steps to healing, and factors to consider when deciding whether to stay together.
Understanding the Impact of Infidelity
Infidelity can take many forms, from emotional affairs to physical betrayals. Regardless of the type, the impact is profound. Here are some common effects:
Breach of Trust: Trust is the cornerstone of any relationship, and infidelity can shatter this trust, leading to feelings of insecurity and doubt.
Emotional Turmoil: Both partners may experience intense emotions, including anger, guilt, shame, and sadness. This emotional upheaval can complicate communication and healing.
Relationship Dynamics: The dynamics between partners often shift drastically after infidelity, requiring both individuals to reassess their feelings and the future of the relationship.
Steps to Overcoming Infidelity
Acknowledge the Pain: Both partners must recognize and validate the pain caused by the infidelity. Ignoring or minimizing these feelings can hinder the healing process.
Open Communication: Honest and transparent communication is essential. The hurt partner should feel free to express their feelings, while the unfaithful partner must be willing to answer questions and share their perspective.
Seek Professional Help: Couples therapy can provide a safe space for both partners to explore their feelings, learn effective communication strategies, and work through the complexities of their relationship.
Take Responsibility: The partner who was unfaithful needs to take responsibility for their actions and acknowledge the hurt caused. This accountability is crucial for rebuilding trust.
Establish Boundaries: Setting clear boundaries moving forward can help both partners feel safer. This may include discussing expectations regarding communication, social interactions, and transparency.
Rebuild Trust: Trust takes time to rebuild. The unfaithful partner should be consistent in their actions, demonstrating reliability and commitment to the healing process.
Focus on Healing: Both partners must actively engage in healing, whether through individual therapy, self-care practices, or spending quality time together. This process is essential for moving forward.
Should You Stay Together?
Deciding whether to stay together after infidelity is a deeply personal choice and depends on various factors:
1. Understanding the Reasons Behind the Infidelity
Reflect on the underlying reasons for the infidelity. Was it a one-time mistake, or does it stem from deeper issues within the relationship? Understanding the context can inform your decision.
2. Evaluating Your Feelings
Consider your emotions and desires. Do you still love your partner? Are you willing to work through the pain, or do you feel too betrayed to continue? Acknowledging your feelings is crucial in making an informed decision.
3. Assessing the Relationship’s Foundation
Evaluate the overall strength of your relationship prior to the infidelity. Was it built on a strong foundation of love, trust, and mutual respect? If so, there may be a greater chance for recovery.
4. Willingness to Work Together
Both partners must be willing to invest time and effort into rebuilding the relationship. If one partner is not committed to the healing process, moving forward may be challenging.
5. Considering the Impact on Family
If children are involved, consider the implications of your decision on their well-being. Staying together or separating can both have significant effects on family dynamics and stability.
Conclusion
Overcoming infidelity is undoubtedly a challenging journey, but it is possible for couples to heal and grow stronger together. The key lies in open communication, taking responsibility, and a mutual commitment to rebuilding trust. Ultimately, the decision to stay together after infidelity is deeply personal and should be based on a thorough understanding of your feelings, relationship dynamics, and willingness to work through the pain. Whether you choose to stay or part ways, prioritizing emotional well-being and growth is essential for both partners.
Strengthening Connections with Your Teenager: Essential Strategies for Parents
Navigating the teenage years can be a particularly tumultuous time for both parents and their adolescents. As teenagers seek to establish their independence and carve out their identities, they often create distance from family, making it imperative for parents to find effective ways to maintain a strong connection. Cultivating and sustaining a robust relationship with your teenager is not only crucial for their emotional well-being but also enhances the overall harmony within the family unit. In this blog post, we will explore various strategies designed to help you forge a deeper bond with your teen.
Understanding the Teenage Experience
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s essential to grasp the unique challenges and experiences that your teenager is navigating during this critical developmental phase:
Identity Exploration: Adolescents are in a constant state of searching for their identities, which can result in mood fluctuations and behavioral changes as they strive for autonomy and self-definition.
Peer Influence: Friends become increasingly significant during these years. Their opinions often take precedence over parental guidance, making it vital for parents to remain relevant and engaged.
Academic and Social Pressures: Teens face a myriad of pressures, from achieving academic excellence to fitting in socially, which can lead to heightened stress and anxiety levels.
Effective Strategies for Staying Connected
Here are several practical and effective methods to help you stay closely connected with your teenager:
1. Foster Open Lines of Communication
Encouraging honest and transparent conversations can create a strong foundation for your relationship.
Engage in Active Listening: Show genuine curiosity about what your teen has to say. Pose open-ended questions and practice listening attentively without interrupting. This approach fosters trust and encourages your teen to share more openly.
Adopt a Non-Judgmental Stance: Approach discussions with an open mind. Make it clear that your teen can share their struggles or mistakes without fear of harsh judgment or reprimand.
2. Invest Quality Time Together
Participating in shared activities can significantly enhance your bond and create cherished memories.
Identify Common Interests: Discover hobbies or activities that you both enjoy, whether it’s cooking, hiking, or binge-watching a favorite series. Set aside regular time for these shared experiences to strengthen your connection.
Be Present in Their Lives: Make an effort to be involved in your teen’s day-to-day activities, whether by attending their games, helping with homework, or simply spending time together at home.
3. Respect Their Need for Independence
While staying involved is essential, it’s equally important to allow your teenager to carve out their own space.
Avoid Overly Controlling Behavior: Grant them the freedom to make their own choices, even if it leads to mistakes. This approach fosters their confidence and helps them learn about responsibility.
Encourage Decision-Making: Involve your teen in family discussions and decisions. This practice not only shows that you value their input but also helps them develop critical thinking and decision-making skills.
4. Leverage Technology Wisely
In today’s digital landscape, technology can serve as a bridge rather than a barrier to connection.
Engage on Social Media: If they’re comfortable, follow your teen on their social media platforms to gain insight into their interests and engage with their online world. This can also serve as a conversation starter.
Utilize Texting and Messaging: Use texting as a tool to stay connected throughout the day. A simple message to express that you’re thinking of them can reinforce your bond and show your support.
5. Demonstrate Empathy and Support
Being empathetic can help your teenager feel understood, valued, and supported.
Acknowledge Their Emotions: Validate their feelings, whether they are experiencing joy, sadness, or anxiety. Let them know that you are there to support them without attempting to "fix" every issue.
Offer Encouragement: Be a source of motivation and support during challenging times, whether related to school, friendships, or personal struggles. Consistently remind them that they can count on you.
6. Establish Boundaries with Love and Clarity
Setting boundaries is crucial for nurturing a healthy relationship.
Communicate Clearly About Expectations: Clearly outline your expectations regarding behavior, responsibilities, and privileges. Ensure your teenager understands the rationale behind these boundaries to foster respect and compliance.
Maintain Consistency: Consistency in enforcing rules and consequences builds trust and helps your teen understand the importance of accountability.
Conclusion
Staying connected with your teenager requires a blend of effort, patience, and understanding. By fostering open communication, spending quality time together, respecting their independence, intelligently utilizing technology, demonstrating empathy, and establishing loving boundaries, you can cultivate a strong and lasting relationship with your teen. Remember, the teenage years are a transitional phase filled with growth and exploration, and your unwavering support can make a significant difference in their lives. Embrace this journey, and watch your relationship with your teenager thrive and flourish!
Navigating Family Conflict: Understanding, Resolution, and Growth
Family conflicts are an inherent aspect of human relationships. Every family experiences disagreements, whether they arise from differing opinions, generational divides, or the inevitable changes life brings. However, the way we approach and resolve these conflicts can significantly influence our relationships and the overall dynamics within the family unit. In this blog post, we will delve into the underlying causes of family conflict, effective strategies for resolution, and the potential for personal and collective growth that can emerge from these challenging situations.
Understanding the Root Causes of Family Conflict
To effectively resolve conflicts, it’s crucial to first comprehend their underlying causes. Some prevalent triggers include:
Diverging Values and Beliefs: Family members often hold varied viewpoints on critical issues such as politics, religion, or lifestyle choices, which can lead to contentious disagreements.
Ineffective Communication: Miscommunication is a common issue that arises when family members fail to articulate their thoughts and emotions clearly, resulting in misunderstandings.
Significant Life Changes: Major events, such as marriage, divorce, the arrival of children, or the loss of a loved one, can alter family dynamics and give rise to conflict.
Generational Differences: The disparity between generations can create tension, especially regarding attitudes toward technology, parenting styles, and social issues.
Unresolved Past Conflicts: Previous grievances may resurface during discussions, intensifying current disagreements.
Strategies for Resolving Family Conflict
Successfully navigating family conflicts requires a blend of patience, empathy, and effective communication. Here are several strategies to facilitate resolution:
Encourage Open Communication: Foster an environment where family members feel comfortable expressing their feelings and opinions. Active listening is vital; ensure everyone has the opportunity to speak without interruptions.
Maintain Composure: Conflicts can evoke strong emotions. Take deep breaths and strive to keep your tone calm. A composed approach can help de-escalate heated situations.
Acknowledge Emotions: Recognize and validate each family member's feelings, even if you do not share the same perspective. Validating emotions fosters understanding and respect among family members.
Identify Common Ground: Focus on shared values or objectives. Finding common interests can serve as a solid foundation for resolving disputes.
Establish Boundaries: If discussions become overly intense, agree to pause the conversation and revisit it later. Setting boundaries can protect relationships while allowing emotions to cool down.
Consider Mediation: In some instances, enlisting a neutral third party can provide valuable perspective and facilitate constructive dialogue, helping to bridge gaps in understanding.
Embrace Forgiveness: Holding onto past grievances can be detrimental to relationships. Encourage family members to practice forgiveness and focus on healing, rather than assigning blame.
The Potential for Personal and Collective Growth
While family conflicts can be daunting, they also offer unique opportunities for growth and development. Here’s how:
Strengthened Bonds: Successfully navigating conflicts can enhance relationships as family members learn to communicate more effectively and support one another during tough times.
Increased Resilience: Overcoming challenges together builds resilience, equipping families to face future conflicts with greater confidence and unity.
Deepened Understanding: Conflicts often lead to profound insights into each other’s perspectives, fostering empathy and mutual respect among family members.
Opportunities for Personal Development: Individuals can acquire valuable conflict resolution skills, enhancing their ability to manage disagreements in various aspects of life.
Conclusion
Family conflict is a natural and unavoidable aspect of relationships, but it doesn’t have to lead to division. By understanding the underlying causes of disagreements and employing effective strategies for resolution, families can not only resolve their issues but also emerge stronger in the process. Remember, it’s not about sidestepping conflict; it’s about how we respond to it that shapes our family dynamics. Embrace the challenges as opportunities for growth, and watch your family flourish!
Strategies to Support your Vagus Nerve: A Guide to Better Health
The vagus nerve is one of the most important nerves in your body, playing a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and immune response. Supporting your vagus nerve can enhance your overall well-being, reduce stress, and promote relaxation. Here’s a guide on how to nurture this vital part of your nervous system.
What is the Vagus Nerve?
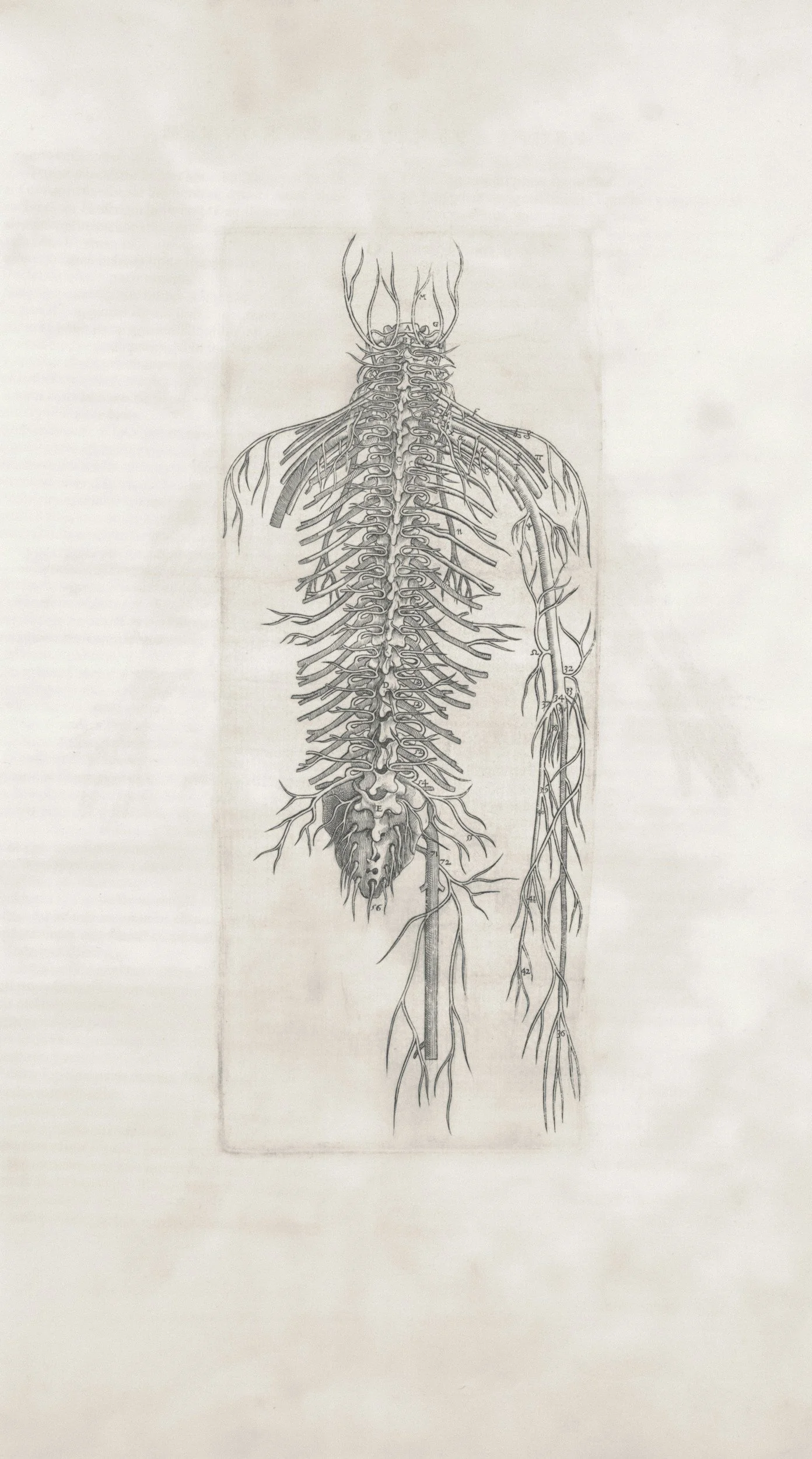
Definition: The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve, extending from the brainstem down to the abdomen, branching out to various organs.
Functions: It is involved in the parasympathetic nervous system, which helps the body rest and digest. It also influences heart rate, blood pressure, and gut health.
Why is Supporting Your Vagus Nerve Important?
Stress Reduction: A well-functioning vagus nerve helps combat stress and anxiety.
Improved Digestion: It aids digestion by stimulating the release of digestive enzymes and promoting gut motility.
Enhanced Mood: A healthy vagus nerve can help improve mood and emotional regulation.
Tips for Supporting Your Vagus Nerve
1. Deep Breathing Exercises
Practicing deep, slow breathing can activate the vagus nerve and stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system.
How to do it: Inhale deeply through your nose for a count of four, hold for four, and exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of six.
2. Meditation and Mindfulness
Engaging in mindfulness practices can help calm the mind and stimulate the vagus nerve.
Try this: Spend 5-10 minutes daily meditating or practicing mindfulness to foster relaxation.
3. Cold Exposure
Cold exposure can activate the vagus nerve, enhancing its function.
Methods: Consider taking cold showers or splashing cold water on your face.
4. Physical Activity
Regular exercise, particularly aerobic activities, can boost vagal tone and improve overall health.
Recommendation: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
5. Singing, Humming, or Chanting
Vocal activities can stimulate the vagus nerve through the muscles in the throat.
Fun idea: Sing your favorite songs or hum while driving!
6. Healthy Diet
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and fiber can support gut health and, in turn, the vagus nerve.
Foods to include: Fatty fish, yogurt, sauerkraut, and leafy greens.
7. Social Connections
Engaging in positive social interactions can stimulate the vagus nerve.
Suggestion: Spend quality time with friends and family or join community groups.
8. Massage and Bodywork
Therapeutic touch, such as massage or acupuncture, can enhance vagal tone and promote relaxation.
Tip: Consider regular massage sessions or practicing self-massage techniques.
Conclusion
Supporting your vagus nerve is a holistic approach to enhancing your health and well-being. By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can improve your body’s stress response, digestion, and emotional health.
Understanding Cognitive Dissonance: The Mental Tug-of-War
Cognitive dissonance is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when we hold two or more contradictory beliefs, values, or ideas simultaneously. This internal conflict can lead to feelings of discomfort and tension, prompting us to adjust our beliefs or behaviors to restore harmony. In this blog, we’ll explore what cognitive dissonance is, how it affects our decision-making, and ways to mitigate its effects.
What is Cognitive Dissonance?
Cognitive dissonance was first introduced by psychologist Leon Festinger in 1957. He described it as the mental discomfort or tension that arises when we experience conflicting thoughts or beliefs. For example, you might value a healthy lifestyle but find yourself indulging in junk food. The clash between your beliefs and actions creates dissonance, leading to feelings of guilt or unease.
Common Examples of Cognitive Dissonance
Smoking and Health: A smoker who knows that smoking is harmful to their health may experience dissonance. To alleviate this discomfort, they might rationalize their behavior by claiming it helps them relax or that they’ll quit soon.
Environmental Concerns: Someone who is environmentally conscious but drives a gas-guzzling car may feel dissonance. They might justify their choice by downplaying the impact of their driving or emphasizing other eco-friendly actions they take.
Purchasing Decisions: After buying an expensive product, a person might experience dissonance if they later find a cheaper alternative. To resolve this, they may convince themselves that the higher price reflects better quality or value.
The Effects of Cognitive Dissonance
Cognitive dissonance can have several effects on our thoughts and behaviors:
Justification: Individuals may justify their contradictory beliefs or actions to reduce discomfort. This can lead to distorted thinking or denial of evidence.
Change in Attitude: To resolve dissonance, people may change their attitudes or beliefs to align more closely with their behaviors. For instance, a person who frequently eats fast food might start to believe that it’s not as unhealthy as they initially thought.
Behavior Modification: In some cases, cognitive dissonance can motivate positive change. If someone feels dissonance about their unhealthy habits, they might decide to adopt a healthier lifestyle to align their actions with their values.
How to Manage Cognitive Dissonance
While cognitive dissonance is a natural part of human psychology, there are strategies to manage its effects:
1. Awareness and Reflection
Recognize when you’re experiencing cognitive dissonance. Reflect on the conflicting beliefs or behaviors and consider why they cause discomfort.
2. Evaluate Your Beliefs
Assess the validity of your beliefs and behaviors. Are they based on facts? Are they serving your well-being? This evaluation can help clarify what changes, if any, are necessary.
3. Seek Consistency
Strive for consistency between your beliefs and actions. If you value health, make conscious choices that align with that belief, such as nutritious eating or regular exercise.
4. Open-Mindedness
Be open to new information and perspectives. Challenging your beliefs can lead to growth and a more nuanced understanding of complex issues.
5. Talk It Out
Discuss your feelings of dissonance with trusted friends or a mental health professional. They can provide support and help you navigate conflicting thoughts.
Conclusion
Cognitive dissonance is a powerful force that shapes our beliefs, decisions, and behaviors. By understanding this phenomenon, we can become more aware of our internal conflicts and work towards aligning our actions with our values. Embracing this journey of self-discovery can lead to personal growth, improved decision-making, and a greater sense of harmony in our lives. Remember, it’s okay to feel discomfort; it’s a sign that you’re navigating the complexities of your beliefs and striving for authenticity.
Understanding Postpartum Intrusive Thoughts: A Compassionate Guide
Bringing a new life into the world is a beautiful experience, but it can also be incredibly overwhelming. For many parents, the postpartum period is marked by a whirlwind of emotions, from joy and love to anxiety and fear. One aspect of postpartum mental health that is often overlooked is the experience of intrusive thoughts. This blog aims to shed light on what postpartum intrusive thoughts are, why they occur, and how to cope with them.
What Are Intrusive Thoughts?
Intrusive thoughts are unwanted, often distressing thoughts or images that can pop into your mind unexpectedly. They may be violent, fearful, or contrary to your values and desires, leaving you feeling confused, ashamed, or scared. During the postpartum period, these thoughts can be particularly intense and may center around fears related to your baby’s safety, your ability to care for them, or even your own mental health.
Examples of Intrusive Thoughts
Common intrusive thoughts during the postpartum period might include:
- Fears of Harm: Worries about accidentally harming your baby, even though you would never intentionally do so.
- Paranoia: Thoughts that something terrible might happen to your baby when you’re not watching.
- Self-Doubt: Feelings of inadequacy or fears that you’re not cut out for motherhood.
It’s crucial to understand that having these thoughts does not mean you will act on them. Many new parents experience intrusive thoughts, and they are often a reflection of the stress, anxiety, and hormonal changes that accompany the postpartum period.
Why Do Intrusive Thoughts Occur?
The reasons behind postpartum intrusive thoughts can vary, but several factors contribute to their occurrence:
- Hormonal Changes: After childbirth, your body undergoes significant hormonal shifts that can affect your mood and mental state.
- Sleep Deprivation: New parents often experience disrupted sleep patterns, which can contribute to anxiety and stress.
- Stress and Anxiety: The pressures of caring for a newborn, adjusting to new routines, and managing expectations can lead to heightened anxiety.
- Personal History: If you have a history of anxiety, depression, or trauma, you may be more susceptible to experiencing intrusive thoughts during the postpartum period.
Coping with Postpartum Intrusive Thoughts
While intrusive thoughts can be distressing, several strategies can help you cope and find relief:
1. Acknowledge Your Thoughts
Recognize that intrusive thoughts are a common experience, especially during the postpartum period. Acknowledging their presence without judgment can help reduce their power over you.
2. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness techniques can help ground you in the present moment. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga can reduce anxiety and create a sense of calm.
3. Talk About It
Sharing your feelings and thoughts with a trusted friend, family member, or therapist can provide relief. You are not alone in this experience, and talking about it can help you feel supported and understood.
4. Seek Professional Help
If intrusive thoughts become overwhelming or interfere with your daily life, consider seeking professional support. A therapist who specializes in postpartum mental health can help you navigate these feelings and develop coping strategies.
5. Join Support Groups
Connecting with other new parents can provide comfort and validation. Many communities offer support groups for postpartum parents where you can share experiences and learn from one another.
6. Prioritize Self-Care
Taking care of yourself is essential.. Self-care is not selfish; it’s a vital part of being able to care for your baby.
When to Seek Help
If you find that intrusive thoughts persist, worsen, or are accompanied by feelings of hopelessness, despair, or an inability to care for your baby, it’s essential to reach out for help. You deserve support and care during this challenging time.
Conclusion
Postpartum intrusive thoughts are a common experience for many new parents, but they can be distressing and isolating. By understanding these thoughts and implementing coping strategies, you can navigate this challenging period with greater ease. Remember, reaching out for help is a sign of strength, and you don’t have to face this journey alone. You are not alone, and there are resources and support available to help you thrive in your new role as a parent.
Understanding Attachment Styles in Relationships: Why They Matter for Conflict Resolution
Relationships can be one of the most rewarding aspects of life, but they can also be a source of conflict and misunderstanding. A key factor influencing how we relate to others is our attachment style. Understanding these styles can provide valuable insights into why we behave the way we do in relationships and how we can navigate conflicts more effectively. In this blog, we’ll explore the different attachment styles, their impact on relationships, and why they matter in conflict resolution.
What Are Attachment Styles?
Attachment theory, developed by psychologist John Bowlby, suggests that the bonds we form in early childhood with our caregivers shape our emotional and relational behaviors throughout life. There are four primary attachment styles:
Secure Attachment:
Individuals with this style feel comfortable with intimacy and are generally trusting. They communicate openly and are able to balance closeness with independence.
Anxious Attachment:
Those with an anxious attachment style often crave closeness but worry about their partner’s commitment. They may display clinginess and seek constant reassurance.
Avoidant Attachment:
Avoidant individuals value independence and often shy away from emotional intimacy. They may struggle to express feelings and can come off as distant or detached.
Fearful-Avoidant (or Disorganized) Attachment:
This style combines aspects of both anxious and avoidant attachments. Individuals may desire connection but feel fearful of it, leading to inconsistent behavior in relationships.
How Attachment Styles Affect Relationships
Understanding attachment styles is crucial for navigating relationships. Here’s how they influence dynamics:
Communication Patterns
Secure individuals tend to communicate openly, facilitating healthy discussions about needs and conflicts.
Anxious individuals may become overly emotional during disagreements, fearing abandonment.
Avoidant individuals often withdraw or shut down when faced with conflict, making it hard to resolve issues.
Fearful-avoidant individuals may oscillate between seeking closeness and withdrawing, leading to confusion and instability.
Conflict Resolution
Each attachment style affects how conflicts are approached and resolved:
Secure individuals are usually adept at resolving conflicts through open dialogue and empathy.
Anxious individuals may heighten tensions by seeking reassurance and fearing negative outcomes.
Avoidant individuals often avoid confrontation, which can leave issues unresolved and lead to resentment.
Fearful-avoidant individuals may react unpredictably, causing further misunderstandings.
Why Understanding Attachment Styles Matters
1. Enhancing Self-Awareness
Recognizing your own attachment style and that of your partner can improve self-awareness. This understanding allows you to recognize triggers during conflicts and respond more thoughtfully rather than reactively.
2. Improving Communication
Knowledge of attachment styles facilitates better communication. For instance, if you know your partner has an anxious attachment style, you can provide reassurance during conflicts, helping to diffuse tension.
3. Building Empathy
Understanding your partner’s attachment style fosters empathy. It encourages you to see their behaviors in the context of their experiences and emotional needs, rather than taking their actions personally.
4. Guiding Conflict Resolution Strategies
Awareness of attachment styles can guide you in employing more effective conflict resolution strategies. For instance:
With an anxious partner, focus on reassurance and validation.
With an avoidant partner, allow space for processing before discussing issues.
Tips for Navigating Conflicts Based on Attachment Styles
Practice Active Listening: Make an effort to understand your partner's perspective without interrupting or judging.
Validate Feelings: Acknowledge the emotions expressed by your partner, regardless of whether you agree with their viewpoint.
Set Boundaries: Be clear about your needs and limits, especially if your partner has an avoidant attachment style.
Seek Professional Help: If conflicts feel overwhelming, consider couples therapy to explore attachment styles and improve communication.
Conclusion
Understanding attachment styles is a powerful tool for fostering healthier relationships and effectively navigating conflicts. By recognizing your own and your partner's attachment styles, you can enhance communication, build empathy, and develop strategies for resolution. Ultimately, this knowledge can transform conflicts from sources of pain into opportunities for growth and stronger connections.
Understanding the Vagus Nerve: Its Importance in Therapy
When it comes to our mental and emotional health, there's a fascinating part of our body that plays a critical role: the vagus nerve. This nerve is often overlooked, but it has a significant impact on our well-being and is increasingly recognized in therapeutic practices. Let's dive into what the vagus nerve is, how it works, and why it matters in therapy.
What is the Vagus Nerve?
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve in the body, extending from the brainstem down to the abdomen, passing through various organs along the way. Its name comes from the Latin word "vagus," which means "wandering," reflecting its extensive reach throughout the body. The vagus nerve is part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate.
Key Functions of the Vagus Nerve
Regulating Heart Rate: The vagus nerve helps slow down the heart rate and promotes relaxation.
Controlling Digestion: It stimulates the digestive tract, aiding in processes like swallowing and food movement through the intestines.
Influencing Mood: The vagus nerve connects the brain to the gut, and research suggests that it plays a role in regulating emotions and stress responses.
The Vagus Nerve and the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system is divided into two main parts:
Sympathetic Nervous System: Often referred to as the "fight or flight" system, it prepares the body to respond to stress or danger by increasing heart rate and energy levels.
Parasympathetic Nervous System: This is the "rest and digest" system, which promotes relaxation, reduces heart rate, and enhances digestion. The vagus nerve is a key player in this system.
When we experience stress or anxiety, the sympathetic nervous system takes over, causing physical symptoms like a racing heart or rapid breathing. The vagus nerve helps counterbalance this reaction, promoting a state of calm and safety.
The Importance of the Vagus Nerve in Therapy
1. Stress Reduction
Therapeutic practices that stimulate the vagus nerve can help reduce stress and anxiety. Techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and certain types of meditation activate the vagus nerve, promoting the parasympathetic response. This can lead to a decrease in feelings of overwhelm and a greater sense of calm.
2. Enhanced Emotional Regulation
Research has shown that a well-functioning vagus nerve is associated with better emotional regulation. Therapies that focus on enhancing vagal tone, such as yoga, mindfulness practices, and even singing or humming, can help individuals manage their emotions more effectively. This is particularly beneficial for those dealing with anxiety, depression, or trauma.
3. Improved Connection Between Body and Mind
The vagus nerve acts as a communication highway between the brain and the body. Therapies that emphasize this connection, such as somatic experiencing or body-centered therapies, can help individuals become more aware of their physical sensations and emotional states. This awareness can lead to deeper insights and healing.
4. Support for Trauma Recovery
Trauma can significantly impact the autonomic nervous system, often causing it to remain in a state of hyperarousal. Techniques that stimulate the vagus nerve can help individuals reconnect with their bodies, process their experiences, and foster a sense of safety and grounding. This is crucial in trauma therapy and recovery.
5. Promoting Overall Well-Being
A well-functioning vagus nerve is linked to improved physical health, including better digestion, lower inflammation, and enhanced immune function. By incorporating vagus nerve stimulation into therapy, individuals may experience not only improved mental health but also physical benefits.
How to Stimulate the Vagus Nerve
Here are some simple techniques that can help activate the vagus nerve:
Deep Breathing: Practice slow, deep breathing—inhale deeply through your nose for a count of four, hold for a moment, and exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of six.
Meditation and Mindfulness: Engage in mindfulness practices that promote relaxation and awareness of the present moment.
Yoga: Certain yoga poses and practices focus on breath and relaxation, helping to stimulate the vagus nerve.
Cold Exposure: Splashing cold water on your face or taking a cold shower can activate the vagus nerve.
Singing or Humming: Vocal activities stimulate the vagus nerve and promote relaxation.
Conclusion
The vagus nerve may not be a household name, but its role in our mental and emotional health is significant. By understanding how this nerve functions and its importance in therapy, we can better appreciate the connection between our bodies and minds. Incorporating techniques that stimulate the vagus nerve into therapeutic practices can lead to enhanced well-being, reduced stress, and improved emotional regulation. If you're seeking support for your mental health, consider discussing these strategies with a therapist who understands the power of the vagus nerve.
Wired for Connection: The Importance of Human Relationships in Mental Health
Human beings are inherently social creatures, wired for connection with one another. This deep-seated need for relationships is not just a quirk of our species; it's a fundamental aspect of our biology and psychology. In this blog, we'll explore why our need for connection matters so much for mental health, the science behind it, and ways to foster those connections in our daily lives.
The Science of Connection
Biological Basis
From an evolutionary standpoint, humans have thrived as social beings. Our ancestors relied on group living for survival, protection, and shared resources. This evolutionary heritage has shaped our brains and bodies:
Neurotransmitters: Oxytocin, often referred to as the "love hormone," plays a crucial role in bonding. Released during social interactions, it promotes feelings of trust and attachment.
Brain Structure: Areas of the brain, such as the prefrontal cortex, are involved in social cognition and understanding others’ emotions. This wiring enables us to empathize and connect with others.
Psychological Perspective
Psychologically, connections with others fulfill essential human needs, as outlined in Maslow's hierarchy of needs. After basic physiological needs, love and belonging are paramount. When these needs are met, individuals experience improved self-esteem and a sense of purpose.
The Impact of Connection on Mental Health
Reducing Loneliness
Loneliness is a significant risk factor for mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. Studies show that individuals with strong social connections are less likely to experience feelings of loneliness. Regular interactions with friends and family can provide emotional support, reducing stress and promoting a positive outlook.
Enhancing Resilience
Social connections can enhance resilience, helping individuals cope with life's challenges. When faced with adversity, having a support system can buffer against stress and provide a sense of security. This resilience is vital for maintaining mental well-being.
Promoting Positive Emotions
Engaging with others can lead to shared experiences and positive emotions. Laughter, joy, and even shared struggles can strengthen bonds. These shared moments contribute to a general sense of happiness and fulfillment, which is crucial for mental health.
Fostering Connections
Prioritize Relationships
To enhance mental health, it’s essential to prioritize relationships. Here are some practical steps:
Reach Out: Don’t hesitate to contact friends or family. A simple message or call can reignite connections.
Join Groups: Participate in community activities, clubs, or classes that align with your interests. This not only fosters new connections but also enhances your social skills.
Be Vulnerable: Sharing your feelings and experiences with trusted individuals can deepen your connections and create a supportive environment.
Digital Connections
In today's digital age, technology can also play a role in fostering connections. Video calls, social media, and online communities can help maintain relationships, especially for those unable to meet in person. However, it's essential to balance online interactions with face-to-face connections when possible.
Conclusion
Our innate wiring for connection is a powerful tool in promoting mental health. By understanding the importance of relationships, we can take proactive steps to cultivate meaningful connections in our lives. As we strengthen our bonds with others, we not only enhance our own well-being but also contribute to a more supportive and connected community.
Final Thoughts
Take a moment today to reach out to someone you care about. The simple act of connection can have profound effects on your mental health and theirs. Let's embrace our wired nature and build a world where connection thrives!
Understanding Anxiety and Depression: What Happens in the Brain Chemically
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health challenges that many people face. While they can feel overwhelming, understanding the chemical processes in the brain can help demystify these conditions. Let’s break down what happens in the brain when someone experiences anxiety and depression, using simple language.
The Basics of Brain Chemistry
Our brains are complex organs that communicate through chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters are like messengers that send signals between brain cells (neurons). When everything is functioning well, these chemicals help regulate our mood, emotions, and overall mental health. However, when there’s an imbalance, it can lead to feelings of anxiety or depression.
Key Neurotransmitters Involved
Serotonin
Role: Often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, serotonin helps regulate mood, sleep, and appetite.
In Anxiety and Depression: Low levels of serotonin are commonly associated with both anxiety and depression. This can lead to feelings of sadness, irritability, and a lack of motivation.
Dopamine
Role: Known as the "reward" neurotransmitter, dopamine is involved in pleasure, motivation, and reward-seeking behavior.
In Anxiety and Depression: Low dopamine levels can contribute to feelings of apathy and lack of enjoyment in activities, which is often seen in depression.
Norepinephrine
Role: This neurotransmitter plays a key role in the body's stress response and helps regulate alertness and arousal.
In Anxiety and Depression: Imbalances in norepinephrine can lead to increased anxiety and heightened stress responses, making it difficult to relax.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Role: GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, which means it helps reduce neuronal excitability.
In Anxiety: Low levels of GABA are linked to increased anxiety, as there isn’t enough calming signal being sent to balance out the excitatory signals.
How Anxiety Affects the Brain
When a person experiences anxiety, their brain goes into a heightened state of alertness. This is often referred to as the "fight or flight" response. Here’s what happens chemically:
Increased Norepinephrine: During moments of anxiety, norepinephrine levels rise, leading to increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and heightened senses.
Low GABA Levels: If GABA levels are low, the brain may struggle to calm itself down, making it harder to relax and feel safe.
Heightened Cortisol Levels: Anxiety can also cause the release of stress hormones, like cortisol, which can further disturb the balance of neurotransmitters.
How Depression Affects the Brain
Depression can feel like a heavy weight, making it hard to find joy in life. Chemically, here’s what happens in the brain:
Low Serotonin and Dopamine: Reduced levels of serotonin can lead to persistent feelings of sadness, while low dopamine levels can strip away motivation and pleasure from everyday activities.
Imbalance of Other Neurotransmitters: The complex interactions between neurotransmitters can create a ripple effect, affecting how we feel and behave.
Structural Changes: Prolonged depression can lead to changes in brain structure, such as reduced volume in certain areas like the hippocampus, which is involved in memory and learning.
The Connection Between Anxiety and Depression
It’s important to note that anxiety and depression often coexist. People who experience anxiety may also develop depression, and vice versa. This is because the same neurotransmitters are involved, and imbalances can feed into each other. For instance:
Chronic Anxiety: Persistent anxiety can lead to exhaustion and feelings of hopelessness, which can contribute to depression.
Depression-Induced Anxiety: On the other hand, feeling depressed can cause anxiety about the future or about one’s ability to cope, creating a cycle that can be hard to break.
What Can Help?
Understanding the chemical processes in the brain can empower individuals to seek help and make informed choices. Here are some common approaches:
Therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can help rewire thought patterns and improve mental health.
Medication: Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can help balance neurotransmitter levels, providing relief from symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and sufficient sleep can positively influence brain chemistry and improve mood.
Mindfulness Practices: Techniques like meditation and deep breathing can help increase GABA levels and reduce anxiety.
Conclusion
Anxiety and depression are complex conditions that involve intricate chemical processes in the brain. By understanding the roles of neurotransmitters and how they impact our emotions, we can better appreciate the challenges of these mental health issues. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety or depression, remember that help is available, and taking steps toward understanding and treatment can make a significant difference.
Coping with Seasonal Affective Disorder: Strategies for Finding Light in the Darkness
As the days grow shorter and the nights stretch longer, many people begin to feel the effects of seasonal changes on their mood and energy levels. For some, this experience goes beyond the typical winter blues and manifests as Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD). This form of depression typically occurs during the fall and winter months, leading to symptoms like low energy, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. If you or someone you know is struggling with SAD, here are some effective strategies for coping and finding light in the darkness.
Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder
Seasonal Affective Disorder is believed to be linked to changes in daylight exposure, which can disrupt the body’s internal clock (circadian rhythms) and affect serotonin levels, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in mood regulation. While SAD can affect anyone, it is more prevalent in women and those living in northern latitudes where daylight hours are significantly reduced during winter.
Common Symptoms of SAD
Low Energy: Feeling sluggish or fatigued, even after a full night’s sleep.
Mood Changes: Increased feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or irritability.
Changes in Sleep Patterns: Sleeping more than usual or experiencing disrupted sleep.
Altered Appetite: Cravings for carbohydrates or weight gain.
Difficulty Concentrating: Finding it hard to focus on tasks or make decisions.
Strategies for Coping with SAD
1. Light Therapy
One of the most effective treatments for SAD is light therapy. This involves using a specialized light box that mimics natural sunlight, which can help regulate your body’s circadian rhythms. Here are some tips for using light therapy:
Timing: Use the light box for about 20-30 minutes each morning, ideally within the first hour of waking.
Distance: Sit about 12-24 inches away from the light box, allowing the light to enter your eyes indirectly.
Consistency: Aim to use the light box daily during the fall and winter months for optimal results.
2. Get Outside
Even on cloudy days, natural sunlight can have a positive effect on your mood. Make an effort to spend time outdoors, especially during midday when sunlight is strongest. Here are some ways to incorporate outdoor time into your routine:
Walk During Lunch: Use your lunch break to take a walk outside, even if it’s just for a few minutes.
Engage in Outdoor Activities: Consider hiking, skiing, or simply enjoying a park to boost your exposure to natural light.
3. Stay Active
Regular physical activity can help alleviate symptoms of depression and boost your mood. Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural mood lifters. Here are some tips for staying active during the winter months:
Find Indoor Activities: Join a gym, take up yoga, or try dance classes to keep moving indoors.
Set Realistic Goals: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week, but find activities that you enjoy to keep you motivated.
4. Maintain a Healthy Diet
What you eat can impact your mood and energy levels. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Here are some dietary tips:
Limit Sugar and Processed Foods: These can lead to energy crashes and mood swings.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to support overall well-being.
Consider Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods like fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds may help improve mood.
5. Connect with Others
Social support is crucial for mental health. Reach out to friends and family, even if it’s just to chat or share a meal. Here are some ways to stay connected:
Plan Regular Gatherings: Schedule regular gatherings with friends or family, whether in person or virtually.
Join Support Groups: Consider joining a support group for individuals experiencing SAD; sharing experiences can be therapeutic.
6. Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practices can help you stay grounded and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression. Consider the following techniques:
Meditation: Spend a few minutes each day practicing mindfulness or guided meditation to calm your mind.
Deep Breathing Exercises: Take time to focus on your breath, inhaling deeply and exhaling slowly to promote relaxation.
7. Seek Professional Help
If your symptoms of SAD are severe or persistent, consider reaching out to a mental health professional. Therapy options such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be particularly effective in treating SAD. A therapist can help you develop coping strategies tailored to your needs.
8. Consider Medication
In some cases, antidepressant medications may be necessary to manage symptoms of SAD. Consult with a healthcare provider to discuss whether medication is a suitable option for you.
Conclusion
Coping with Seasonal Affective Disorder can be challenging, but with the right strategies, it is possible to navigate the winter months more positively. Incorporating light therapy, staying active, and seeking social connections can make a significant difference in your overall well-being. Remember, you are not alone in this experience, and seeking support can lead to improved mental health and a brighter outlook. Embrace the light wherever you can, and take proactive steps to nurture your mental health during the darker months.